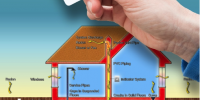
Radon is a radioactive gas produced when uranium breaks down in water, rocks, and soil. Certain building materials (such as stones used for a fireplace) may give off radon, and radon can also enter your home through well water if you live in an area with a lot of granite or shale. However, the most common method of how radon enters your home is by passing through the soil and your house’s foundation.
Radon and Your Home’s Foundation
One of the causes of radon in homes is when it rides on soil gasses that pass into your house through cracks in the foundation or a part of the home that is in direct contact with the soil, such as a crawl space or sump pump pit. However, even if your home is well-sealed, it’s still possible for radon gas to penetrate concrete foundations and most floor coverings. Other potential entry points that explain how radon gas gets into homes include mortar joints, floor-wall joints, and loose-fitting pipe penetrations.
The Movement of Radon Gas
Now that we’ve identified radon entry points, you may be wondering how radon enters your home from the soil in the first place. This upward movement is caused by a difference in pressure between the air in your home and the soil underneath it. Air pressure in the home is lower than in the ground, which causes radon to get pulled up into your home (think of a vacuum cleaner sucking up dirt and debris in its immediate vicinity).
Radon levels are highest at the point where this radioactive gas enters the home, which in many cases is the basement. This is what causes radon in homes to measure highest in basements and first floors. It becomes more diluted as it rises because it mixes with more fresh air. However, radon levels could be high anywhere in your home, and it’s important to conduct a radon test even if your basement isn’t a living area.
Homes without a basement (often called “on slab”) are especially problematic, as all the living and sleeping areas are now just above the soil, putting the radon particles closer to direct breathing spaces.
Radon Levels in Your Home Are High: What’s Next?
When breathed in, the radioactive particles in the radon gas damage the tissue in the lungs. Over time this can cause lung cancer, so
if you discover radon levels in your home are high, it’s important to take action to reduce those levels. Attempting to seal up the causes of radon in homes, such as the entry points mentioned above, is not considered an effective long-tem solution. You can permanently handle radon in your home by having a radon mitigation system installed by an expert. A radon mitigation system will suction the soil below your home, drawing radon gas through a pipe and discharging it above the roof edge so that you and your family aren’t breathing it in.
Because radioactive materials are being handled, it is important that a professional is involved in the system installation.